Route Groups
In the app directory, nested folders are typically mapped to URL paths. However, you can designate a folder as a Route Group to exclude it from the route’s URL path.
This is useful when you want to organize your routes into subdirectories without changing the URL structure. Route Groups allow you to organize your route segments and project files into logical groups without affecting the URL path structure.
Route groups are useful for:
- Organizing routes into groups (e.g., by style section, intent, or team).
- Enabling nested layouts in the same route segment level.
A route group can be created by wrapping a folder’s name in parenthesis: (folderName)
Organize routes without affecting the URL path
To organize routes without affecting the URL, create a group to keep related routes together. The folders in parenthesis will be omitted from the URL.
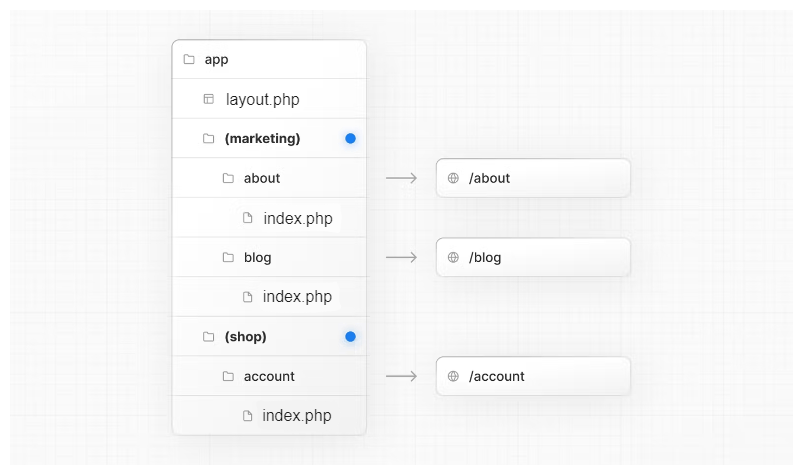
app/
├── layout.php
├── (marketing)/
│ ├── about/
│ │ └── index.php → /about
│ ├── blog/
│ │ └── index.php → /blog
├── (shop)/
│ └── account/
│ └── index.php → /account
Even though routes inside (marketing) and (shop) share the same URL hierarchy, you can create a different layout for each group by adding a layout.php file inside their folders.
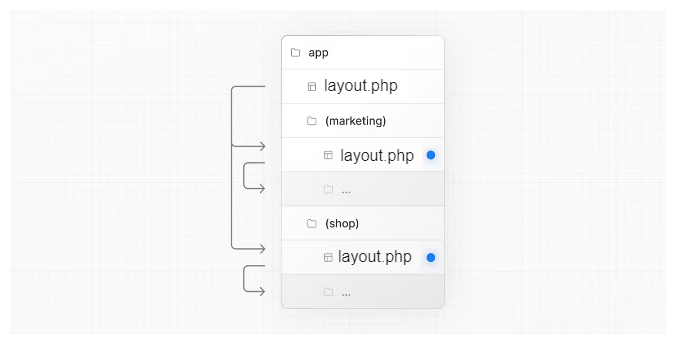
Opting specific segments into a layout
To opt specific routes into a layout, create a new route group and move the routes that share the same layout into the group. Routes outside of the group will not share the layout.
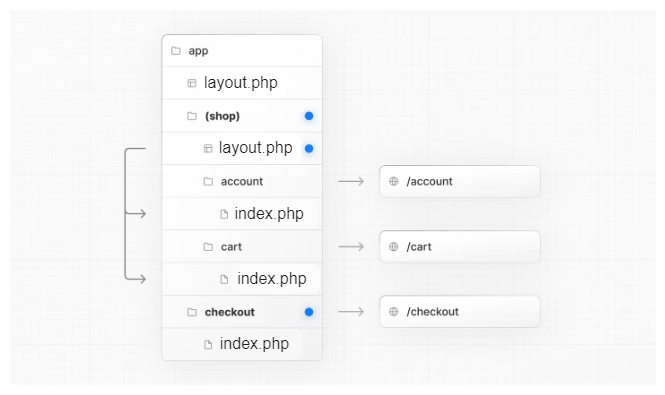
app/
├── layout.php
├── (shop)/
│ ├── layout.php
│ ├── account/
│ │ └── index.php → /account
│ ├── cart/
│ │ └── index.php → /cart
├── checkout/
│ └── index.php → /checkout
Good to know
- The naming of route groups has no special significance other than for organization. They do not affect the URL path.
- Routes that include a route group should not resolve to the same URL path as other routes. For example, since route groups don't affect URL structure, (marketing)/about/index.php and (shop)/about/index.php would both resolve to /about and cause an error.
- Navigating across multiple root layouts will cause a full page load (as opposed to a client-side navigation). For example, navigating from /cart that uses app/(shop)/layout.php to /blog that uses app/(marketing)/layout.php will cause a full page load. This only applies to multiple root layouts.